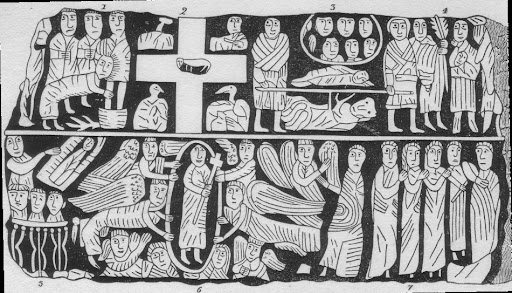
The Wirksworth Stone must be one of the most remarkable examples of sculpture from the Saxon era in England. Discovered in 1820 face down, buried under the church floor, it is thought to have been the lid of a sarcophagus belonging to an early saint, possibly Betti. It dates from about 700 CE, and displays a sophisticated iconography which reveals a strong Eastern influence e.g. the use of the Greek cross with equal arms. Perhaps the most interesting question is who produced this work 1,300 years ago, and was it carried here or made on the spot?

Clearly the present thirteenth-century building (above) was not the first on this site; in fact the name of the local river, Ecclesbourne, suggest a very ancient foundation, probably a minster church for the whole wapentake of Wirksworth. Just as churches were built by travelling stone masons we can assume that sculpture like this was the work of itinerant artists, who would also produce crosses like those at Bradbourne and Eyam. It is claimed that the Wirksworth stone shows the work of two masons, the one responsible for the lower half being more skilled than his (or her) workmate. Although overall the workmanship is somewhat crude, the scenes portrayed cover the whole range of Christian teaching.

The ascent of Christ, in mandala (detail)
The left hand side of the stone has been broken off, so originally there were ten scenes but now only eight are visible. It appears that the stone should be read vertically, top to bottom, rather than left to right like a modern comic strip. So the top left scene shows Christ washing the feet of the disciples, and the one below the Harrowing of Hell, when the crucified Christ is supposed to have descended into Hades. The next pair are clearly the Crucifixion (with four evangelists) paired with the Ascension below. The third scene on the top represents the death of the Virgin, and below this the Annunciation is shown, with Mary seated. The final scene on top is the Presentation of the infant Christ in the temple, and under this the disciples prepare for their preaching mission (note the figure in the boat). Overall, and assuming the missing section showed the Nativity and the Baptism of Christ, the whole panel presents a remarkable statement of fundamental Christian beliefs. The position of Wirksworth on the Derbyshire Portway reinforces the theory that this was the work of travelling craftsmen, bringing the essentials of their religion in pictorial form to the (presumably) illiterate of the Peak.


Hi Stephen, we met at the Wirksworth book festival. I really enjoyed your talk and your guide to the Portway when we walked it a few years ago. These blog posts are great too. I’ve read a few now, and came across this one when researching for a guided walk I’m leading in Wirksworth this weekend.
It just occurred to me… I’ve always assumed the Wirksworth Stone was carved in local limestone. It’s roughly the right colour. But your question about where it was made left me wondering… as if it was made of local stone, we’d be more sure it was made here, not carried in.
Do you know what stone it’s carved in? As now I’m looking online, I can’t find any reference to its material.
I’m only just realising I had no basis for my unconscious assumption about it being limestone!
LikeLike