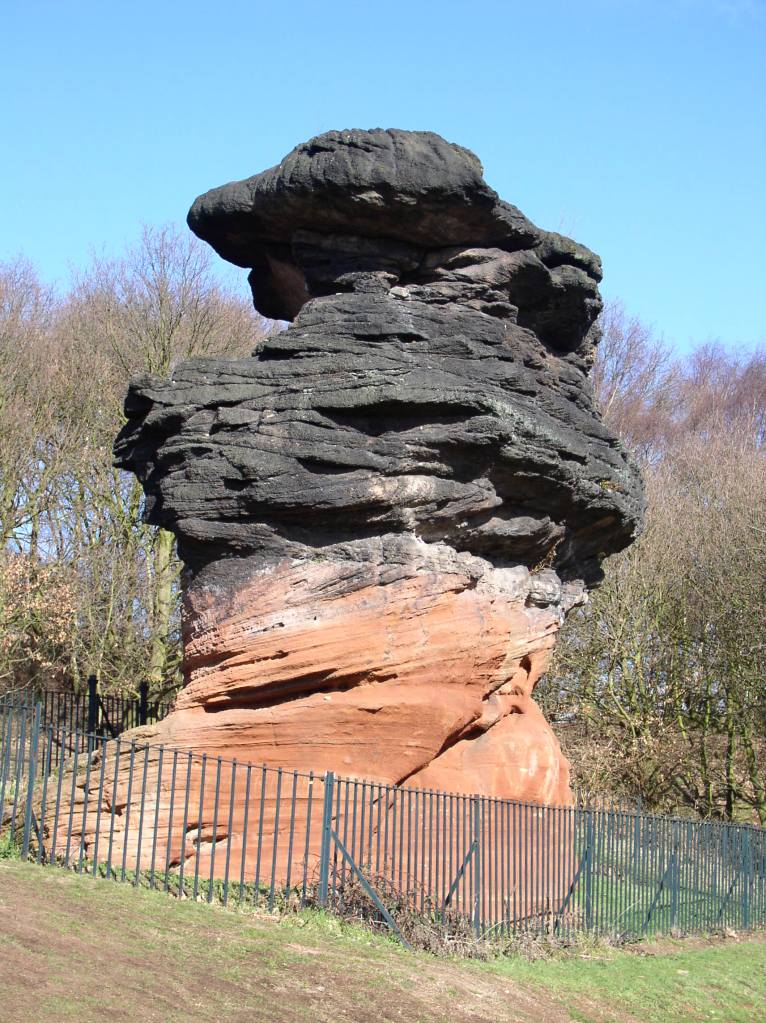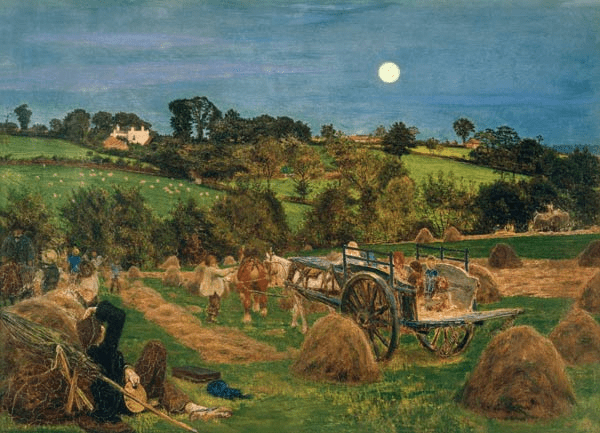
By 1878 the painter Ford Madox Brown, at the age of 57, was suffering from severe gout, that classic Victorian ailment. His wife and model Emma had become alcoholic, probably as a result of the cuckoo in their nest, the 37-year-old poet Mathilde Blind, the object of his unresolved passion. It was Mathilde who proposed a family holiday in the fashionable resort of Matlock Bath that summer, along with his daughter Lucy and Lucy’s husband Frank. They would presumably have come by the Midland railway from their London home, and then by station fly to the house they had rented, ‘Belmont’, high above the river on Waterloo Road. The August weather allowed the younger members of the party to enjoy long walks along the valley, but Madox Brown was unable to join them, being literally bedridden with gout for most of the holiday. Perhaps that’s why he produced no Derbyshire paintings to rival those he painted in the London area, such as The Hayfield (above). As an associate of the Pre-Raphaelites he was faithful to their principle of working outdoors for authentic lighting effects, as can be seen in his iconic painting The Last of England.
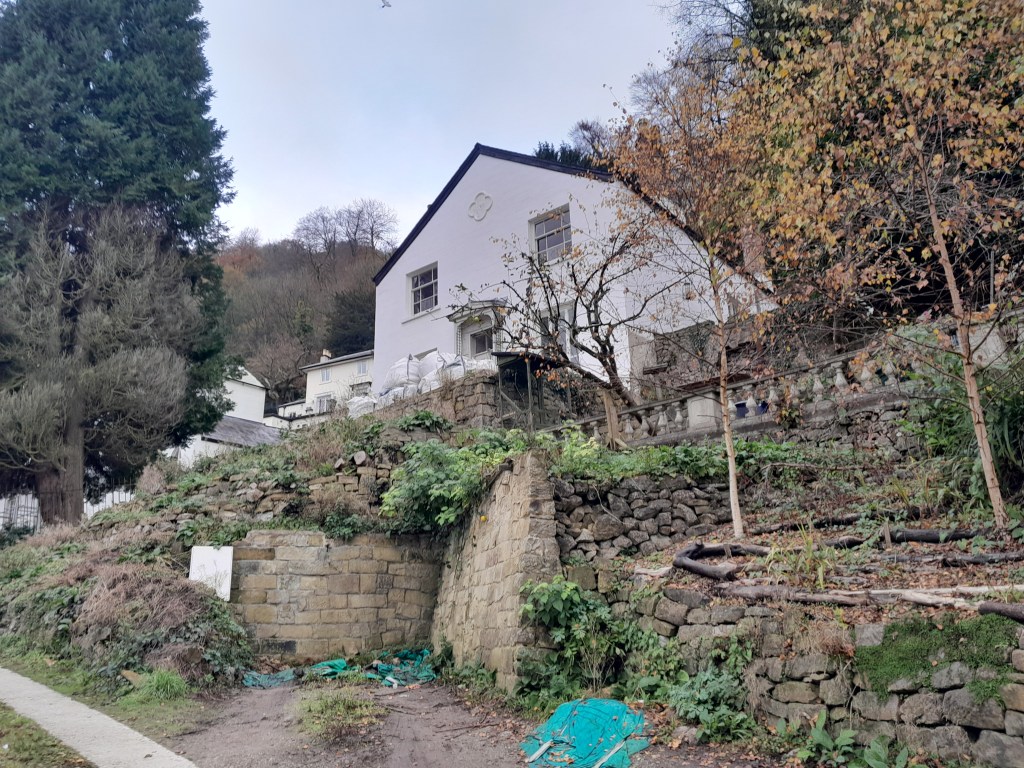

Belmont survives, a Grade II listed building which was constructed in 1847, one of the earliest houses on Waterloo Road. By 2021 it was in a dilapidated condition, and was auctioned that year for £203,000. Today it is freshly renovated and repainted, tucked away off the road, with views over towards High Tor.

This self-portrait was made about the same time as Brown’s visit to Matlock. His lengthy beard and severe expression give him a patriarchal air, but friends such as Rossetti claimed that he was genial and sociable. He certainly had a difficult life: his parents were English but led a wandering life in the Low Countries for economy; his mother and sister both died before he was 20 and his father shortly after. He married a cousin, Elisabeth Bromley, who died of TB six years later, and then married his model, Emma, who posed as the emigrating wife in The Last of England. Her drinking increased as he became infatuated with two much younger and strikingly attractive women, Maria Spartali and Mathilde Blind, both part of London’s intellectual immigrant community, Marie from Greece and Mathilde from the German-speaking states. Yet neither of these relationships appear to have been consumated, while their consequence was to make all parties miserable – welcome to Bohemia!