A recent winter view of Youlgreave
Winter has never been the best season for travel, but in the past it must have been far more difficult than today. Not only were roads much worse, but at times the weather seems to have been much colder. Especially in the upland areas of Derbyshire farms and villages were likely to be cut off by snowdrifts, with the constant threat of hunger if people were unable to reach markets. According to the Youlgreave Churchwardens’ records:
This year 1614 began the greatyst snow that ever fell within many memorye. And for heaps or drifts of snow they were very deep; so that passengers both horse and foot, passed over gates and hedges and walls it fell at ten severall times, and the last was the greatest … it continued by daily increasing until 12th day of March …

Snowdrifts at Farley above Matlock in 1947
The freezing winter of 1947, still within living memory, was made worse by the decrepit nature of the country’s infrastructure, worn out by years of war. Heavy snow began in late January and continued well into March. Conditions were primitive in many parts of Derbyshire, as recorded by a Mrs Alsop of Hulland Ward near Ashbourne:
All the local men were called by the council to leave their jobs to help clear the roads. This was all done by hand and shovels – no mechanical diggers in those days. The strong northeast, gale-force winds daily filled the roads. The men worked seven days a week for six weeks or more. … Younger folk trudged to Ashbourne (five miles or more) for bread.
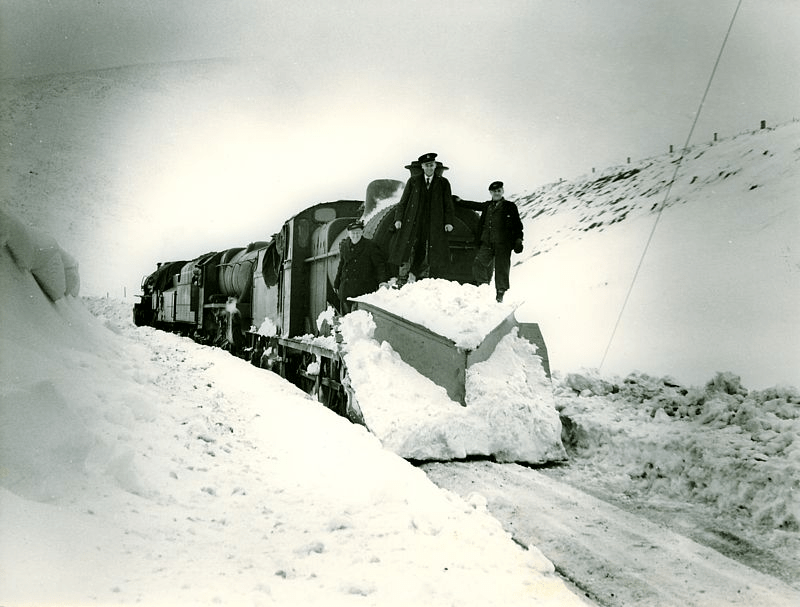
In the Peak conditions were worse and neither roads or railways could be kept open, despite heroic efforts. Around Buxton, Longnor and the Staffordshire side of the Dove valley bombers were used to supply isolated settlements. Thousands of pounds of flour, sugar, jam and tinned goods were dropped by parachute. Tragically, one of the planes crashed on Grindon Moor, killing all eight on board. The weather finally relented in early March, when the landlord and landlady of the Barrel Inn at Bretton could leave the bedroom where they had been trapped for the past five weeks, having been dug out by rescuers.
Source: The Derbyshire and Nottinghamshire Weather Book (1994) Markam, L.








