For thousands of years goods had to be carried by roads, and a horse and cart could move about a ton of stone or coal. But with industrial growth in the eighteenth century increasing demand for raw materials canals became a feasible mode of transport, a horse-drawn narrowboat could carry 30 tons. From about 1760 the canal network grew quickly, and by 1788 a route was planned from Cromford to Langley Mill, where it would link up with the Erewash Canal and so gain access to the Trent basin. Local entrepreneurs such as Gell at Hopton and lead smelters at Lea and Crich were keen to promote this facility for their minerals, while also benefiting from cheaper coal deliveries.

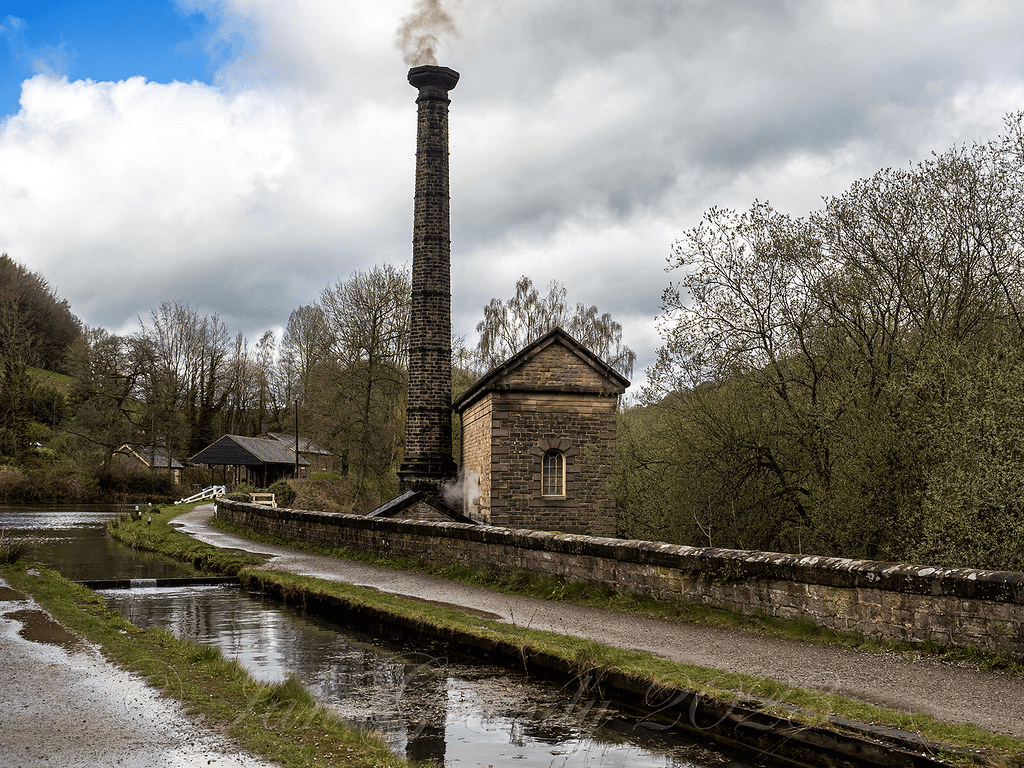
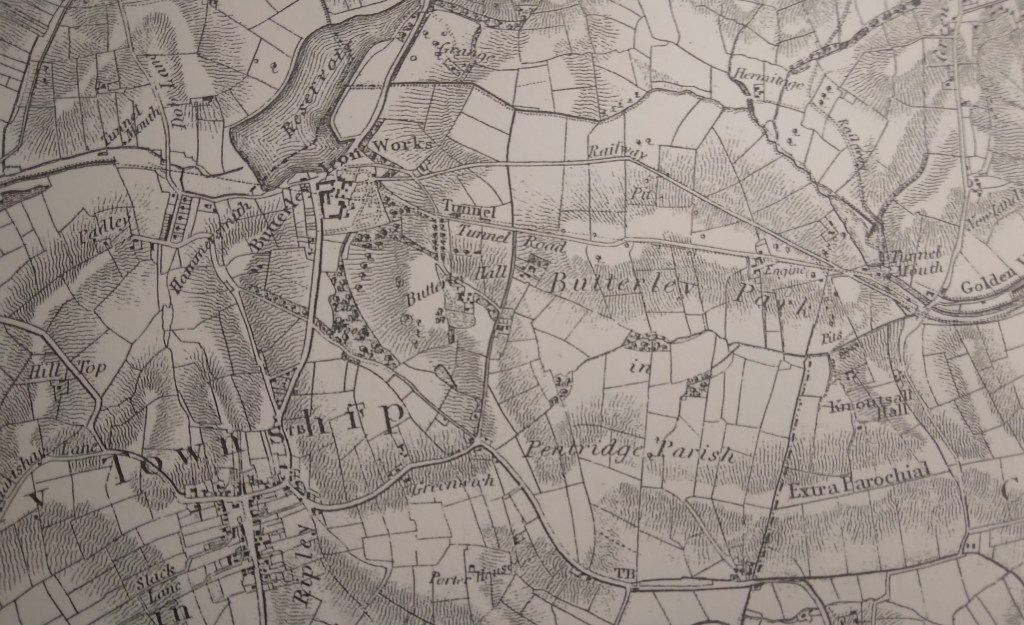
Building the canal with nothing more advanced than shovels and wheelbarrows seems remarkable today, especially as aqueducts were needed to cross the Derwent by the Leawood pump house and over the Amber (above – the railway came later!). In addition, Butterley tunnel, about 3,000 yards long, proved difficult to cut and maintain. The entire route from Cromford to the Butterley tunnel was on a level, so no locks were needed. This saved water, which was always an issue given the original supply was the Bonsall Brook, shared with Arkwright’s mill. The pump house was a later addition, lifting water from the Derwent. The estimate for the canal’s construction was about £42,000, but inevitably the actual cost was nearly twice this when it finally opened in 1794.

The sign in the photo gives a good idea of the goods carried by the canal: not just coal and coke but also salt, pipes and straw. However, by the time this was taken the canal was in decline: from the 1850s the railway was providing a cheaper and faster service. At its peak in the early 1800s the canal carried 300,000 tons per year, and paid shareholders a whopping 20%. But in 1852, as profits declined, the canal was sold to its railway rival – which was already operating the High Peak line from Cromford to Manchester. The tunnel suffered several rock falls, which finally closed the through route in 1900, though local traffic between Hartsay and Cromford continued until 1944. It seems curious that such a substantial, splendid piece of engineering should have such a short life, effectively becoming redundant after only 50 years!