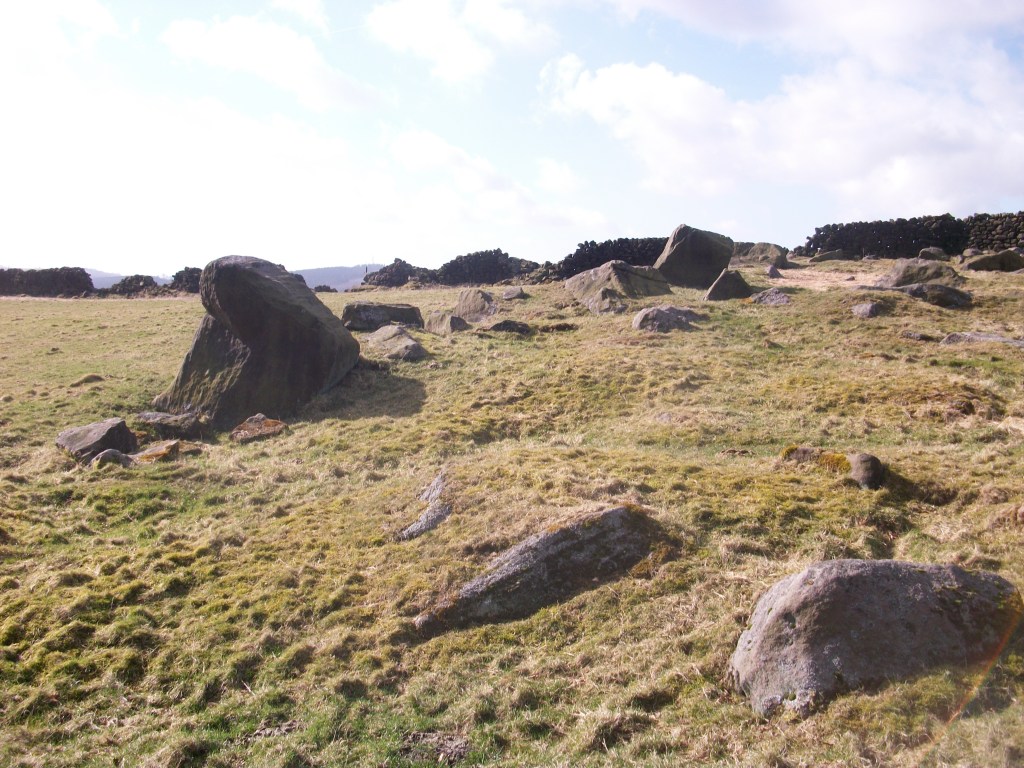
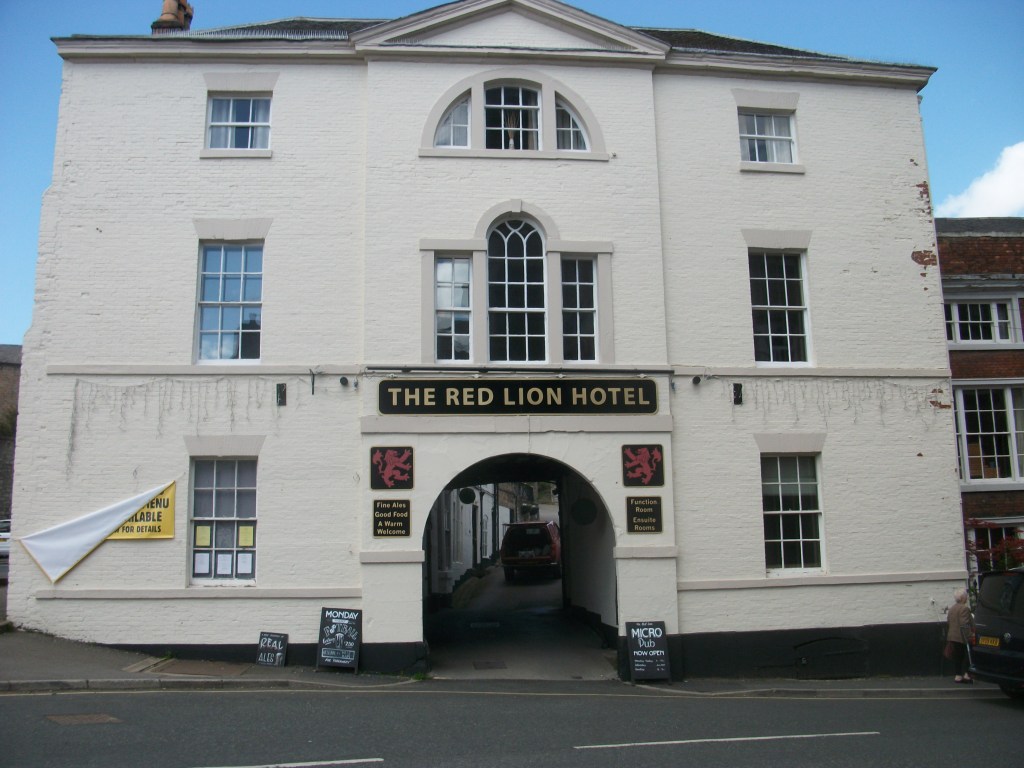
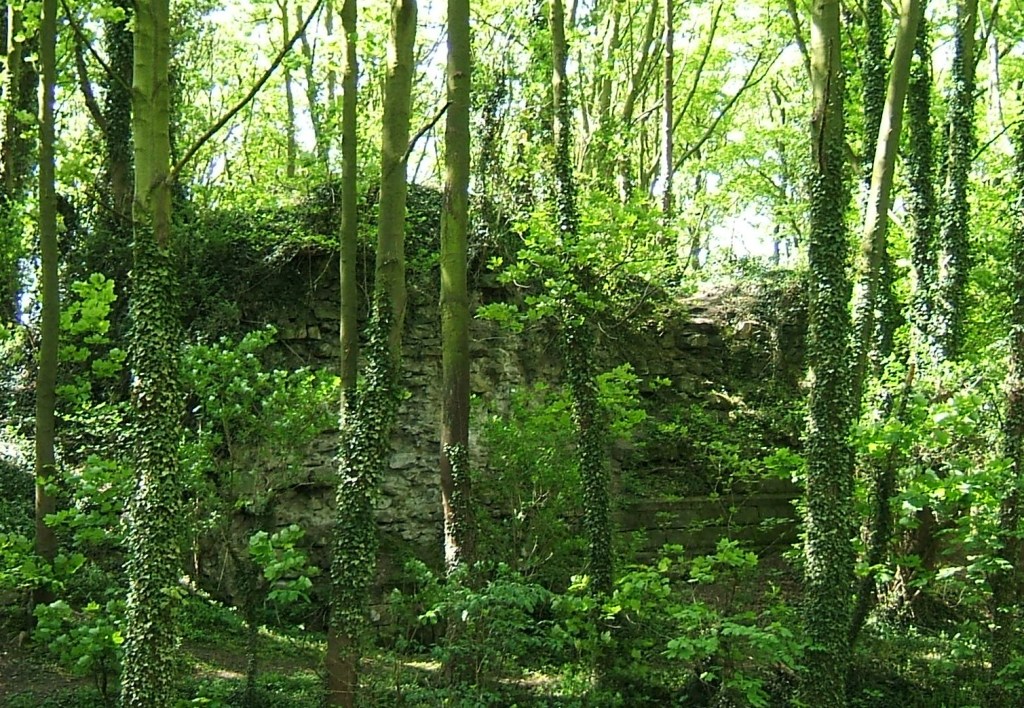
Starting from Whatstandwell Bridge, if you follow the track from the hamlet of Robin Hood up through the quarry and wood to Wakebridge, and then on past Wakebridge Farm up to the top of the hill, the route finally levels off and you come to Shuckstone Fields, behind Holly Grange Farm and above Lea. This large field contains the intersection of five footpaths, and Shuckstone Cross must have marked this point. Today only the base remains, and the markings on this are illegible, but according to local historian George Wrigglesworth the four sides were marked C (for Crich) A (possibly Ashover) M (Mansfield or Matlock) and W (Wirksworth). In the late eighteenth century a pot containing Roman coins was dug up here, presumably buried by someone wanting a clear marker for their savings. Not far away is a ‘Holy Well’ of three compartments, which could have offered refreshment for travellers.

The term ‘cross’ can be misleading: the crosses found in country churchyards, as at Eyam, had a cross shape and were often preaching crosses, while a cross as at Shuckstone was simply a stone shaft held in a square base which acted as a waymark or signpost. This marker would have been clearly visible at this high point (nearly 900 feet), which was moorland until a couple of hundred years ago: the 1791 map shows that the area was the southern tip of East Moor, an expanse of rough pasture which stretched from here north towards Chatsworth and then Sheffield.
The Cross may have also been a boundary marker, since the same map (Burdett’s) also shows that the track up from the Derwent runs along the old wapentake boundary, with the wapentakes of Wirksworth to the west and Morleyston to the east. According to Kenneth Cameron, (The Place-names of Derbyshire Part 2) the name ‘Shuckstone’ is fairly recent, and older records, going back to the Domesday Book, refer to this spot as ‘Shuckthorn’ or similar, meaning the Devil’s thorn tree. This is certainly a location well worth visiting, but probably not on a dark night.