Few people outside the Midlands have heard of this Saxon saint, but in Derbyshire he is commemorated by two churches, a well and a street, besides being the patron saint of the city of Derby. As with many saints from the Saxon period it is hard to sort the legends from the facts, but apparently he was King of Northumbria in the late eighth century until he was forced to flee south into Mercia when a rival branch of his family took the throne. He was murdered by Northumbrian agents about 800 CE and buried in Shropshire, after which a cult grew up around his name due to his reputation for acts of charity.
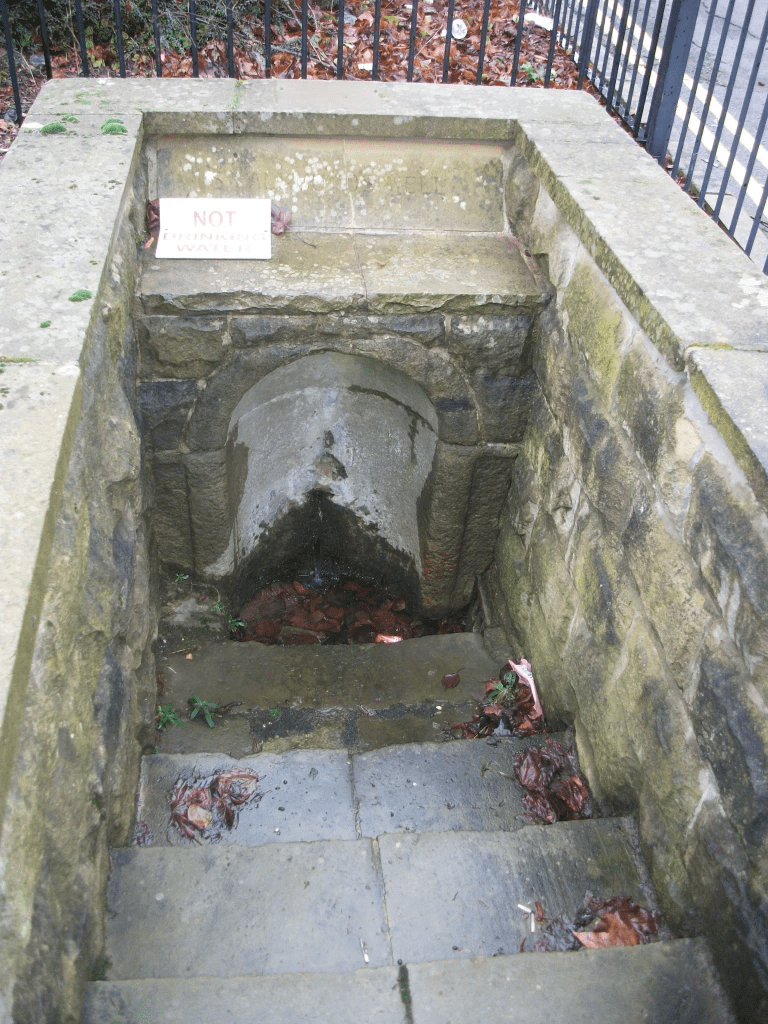

His remains were removed to Derby in 1140 and reburied in the church dedicated to him, which had a Saxon foundation, near the modern Jury’s Inn hotel. This church was re-built in the mid-nineteenth century but demolished in 1968 as part of Derby’s inner ring road development. A stone plaque marks the site today. The only positive aspect of this piece of urban vandalism (widely criticised at the time) was the discovery of what is believed to be St Alkmund’s stone sarcophagus, a fine piece of Anglo-Saxon stone carving, now in Derby museum. We must assume that this was brought from Shropshire, along with the saint’s remains, in the twelfth century, though this must have been a difficult operation, weighing as it does about a ton. The most likely route would have been by river, as the church was only two hundred yards from the Derwent. Not far away from the church, at the bottom of Well Street, which runs off North Parade, is St Alkmund’s Well. Now protected by iron railings, this had a rural setting until the early nineteenth century as it was in St Helen’s park. Today it must be one of the few holy wells in an urban setting, and was at one time the focus of church procession and well dressing.

St Alkmund’s in Derby was conveniently near Ryknield Street, the old Roman road, which would have allowed regional pilgrims to travel to the shrine, while only a few miles north is another church with the same rare dedication, at Duffield. Here the church is sited curiously detached from the town and close to the river. Although the present church building is post-Conquest, this must have been a Saxon foundation in what was originally a very large parish. It is thought that the church’s siting may have been due to the use of the Derwent for baptism, although this has also led to severe and quite regular flooding of the building.