These unusually colorful figures on the Babington tomb at Ashover are a reminder of a long-distance packhorse route that can be traced as far as Wirksworth to the west. Ashover parish used to be much larger, and included Holloway, Lea and Dethick, the home of the Babingtons. St John’s church at Dethick was built as a private chapel for the manor, but Ashover had to be used for burials. Most of the route can be comfortably walked today; leaving Ashover by the track beside the Old Poet’s Corner pub which drops to a bridge over the Amber, and then provides a steep climb up a remarkably complete stone causeway (below).

‘Causeys’ like this are found all over Derbyshire and are about two feet wide, thus providing a solid surface for horses’ feet at minimal expense. The track continues to climb towards Ravensnest and then meets Holestone Gate Road at the top. From there it’s road walking to the B6014 and along Lickpenny Lane to the Matlock-Alfreton road. At this point a guidestoop can be seen on the verge, dated 1710, marked A+P for Ashover Parish. Wirksworth is one of the directions shown, via Dethick Lane (NB the stoop has been moved from its original position, but not significantly). Dethick Lane is partly a holloway, Cross Lane marks the site of an old cross (only the base remains), and beyond the church the path leads down to a crossing of the Lea Brook on stepping stones, then uphill to cross Hearthstone Lane and down to Cromford Station and bridge.
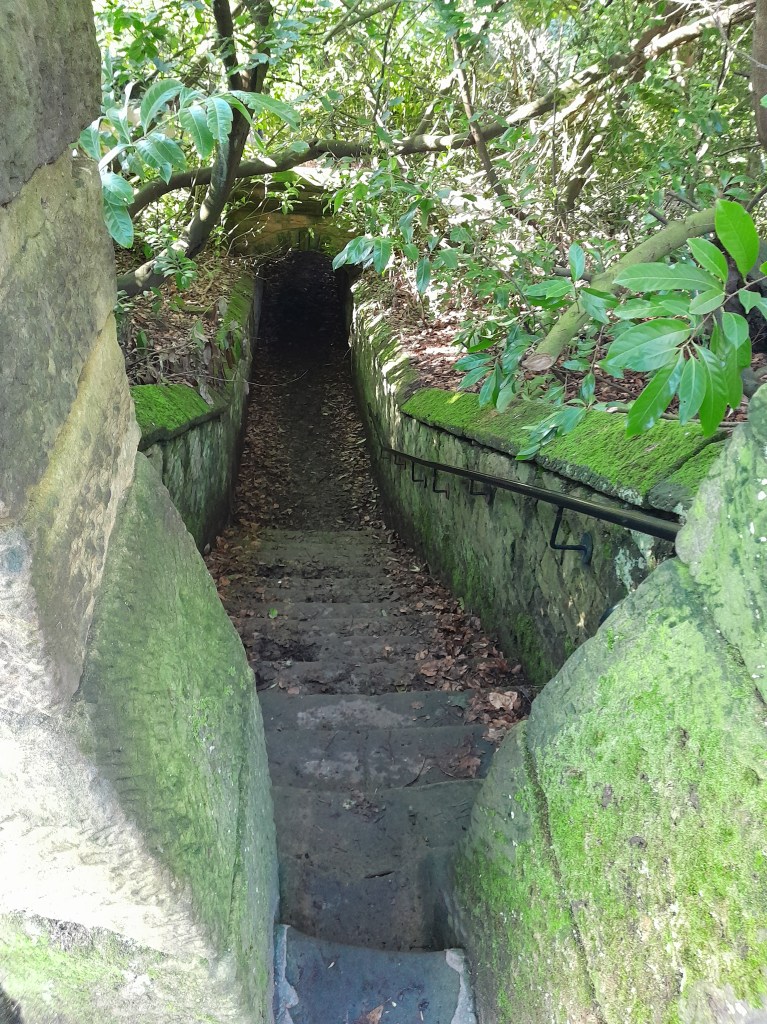

Where did the route go to the east from Ashover? One likely possibility is the footpath which starts beside the Black Swan and runs up through the grounds of Eastwood Grange, today a school but which must have been built in Victorian times as a substantial private villa. The route (even if no longer used by packhorses) was clearly significant enough to be given a well-engineered stone-lined route through the gardens of the Grange, as can be seen above. Beyond this the path continues steeply up to the summit of Farhill, a popular viewpoint at 299 metres, from where Hardwick Hall, Chesterfield and Sheffield can be seen.