
With the opening of the North Midland Railway line from Derby towards Chesterfield in 1840 the pattern of transport in the area was transformed. Faster and cheaper movement of both freight and passengers would lead to the eclipse of the turnpike roads. But in the very early period rail travel was regarded as exotic and probably dangerous. A gentleman’s private coach could be loaded onto a flatbed truck, saving his family the need to mix with the hoipolloi. Yet railway companies were keen to make travel a comfortable experience for their better class of customer, in a way that’s hard to imagine today.

This is demonstrated by the facilities at South Wingfield Station, recently restored to its original form by Derbyshire Historic Buildings Trust, working with local volunteers, and with a substantial grant from the Lottery Heritage Fund. This was one of the earliest stations in the country, designed by architect Francis Thompson. The building had a booking office and two waiting rooms, complete with handsome fireplaces, all maintained by several staff, including a stationmaster who lived in a nearby house. Today’s travellers, huddled in a draughty platform shelter, can only dream of such luxury!
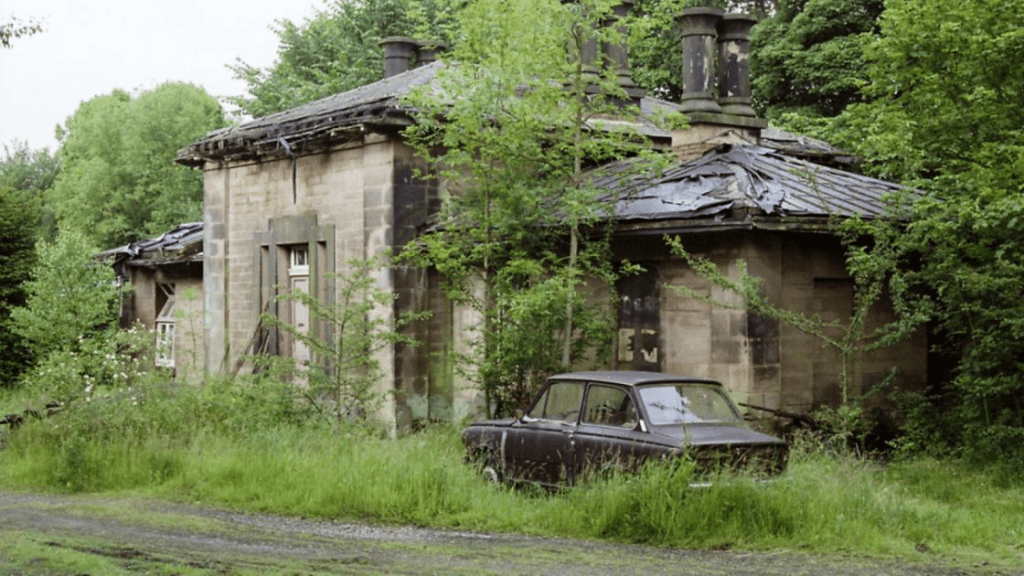
South Wingfield Station, which became redundant in the 1960s, is some distance from its village, yet it was originally advertised as convenient for Alfreton too! This was because Robert Stephenson engineered the line to run up the gentle slope of the Derwent and Amber valleys, since early locomotives weren’t powerful enough to deal with steep climbs. The Nottingham to Newhaven turnpike ran near the station, heading for Crich, and would have another twenty or so years of life before the spreading railway network put it out of business.
South Wingfield Station can be seen from the public footpath which runs through the station yard. See the website below for more background information and details of guided tours:
https://www.derbyshirehistoricbuildingstrust.org.uk/wingfield-station-our-project







