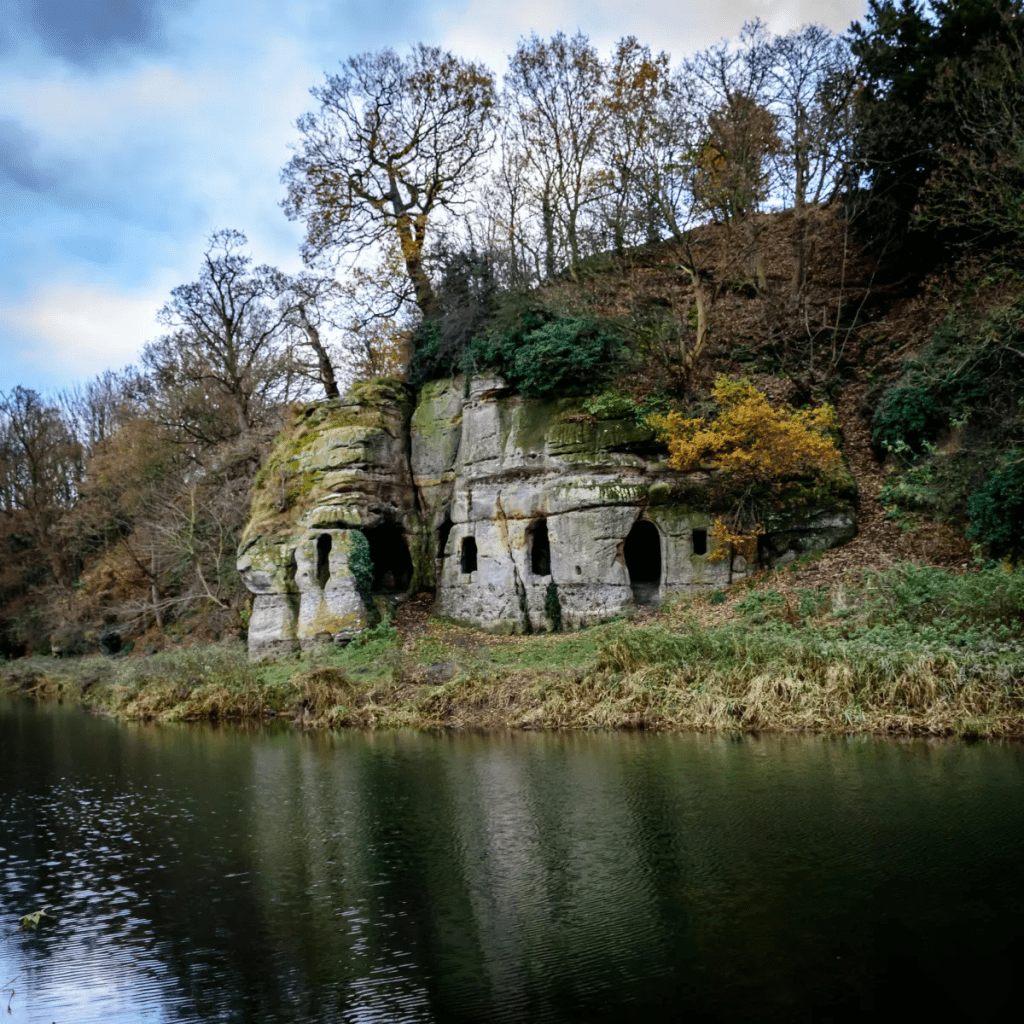
Anchor Church today
On the steep south bank of the River Trent, a short walk from Ingleby village, this rock-cut structure may have been used since the ninth century. Although the photo suggests that the river comes to the doorstep, in fact this is a pond, probably a remnant of an earlier course of the river, which has now shifted into a new channel to the north. Clearly cut out of sandstone, it is now thought that this was the refuge of the Saxon saint Hardulph, who had been deposed as King of Northumbria in 806 CE. He was buried at the nearby church of Breedon on the Hill, which is dedicated to him.

An interior view
The next stage in its history began in the thirteenth century, when it was the cell of an anchorite or hermit, hence the name Anchor. It is a mistake to imagine a hermit as a wild and solitary figure, leading a life of lonely meditation, and shunning contact with the world. Repton church and priory was quite near and may have been linked to the hermitage. It is also possible that the hermit was a part-time ferryman, at a time when the Trent ran at the foot of the rock. Burdett’s map of 1767 shows two ferry crossings nearby and upstream, one at Twyford and the other at Willington. Ferries were clearly quite common up to the nineteenth century, as a simple alternative to a costly bridge. Not only would this have given the hermit a useful function, but it could also have provided a small income.

An eighteenth century idyll
The hermitage presumably fell out of use with the dissolution of the monasteries in 1538, and the next records are from the eighteenth century when the landowners, the Burdett family of Foremark Hall, modified the structure for use as a summerhouse. This provided a suitably Gothic atmosphere for elegant alfresco parties, as can be seen in the print above. Sir Francis Burdett was a notable Radical who was actually briefly imprisoned in the Tower of London for libelling the House of Commons. Today the site is Grade II listed, and can be visited by footpath from Ingleby.